Ocean County Public Health Profile Report
Incidence of Breast Cancer in Females: Age-Adjusted Rate per 100,000, 2014-2018
Ocean 134.595% Confidence Interval (129.2 - 139.9)Description of the Confidence IntervalThe confidence interval indicates the range of probable true values for the level of risk in the community.
A value of "NA" (Not Available) will appear if the confidence interval was not published with the NJSHAD indicator data for this measure.State 137.2U.S. NA NA=Data not available.Ocean Compared to State
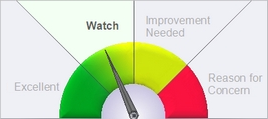
Description of GaugeDescription of the Gauge
This graphic is based on the county data to the left. It compares the county value of this indicator to the state overall value.- Excellent = The county's value on this indicator is BETTER than the state value, and the difference IS statistically significant.
- Watch = The county's value is BETTER than state value, but the difference IS NOT statistically significant.
- Improvement Needed = The county's value on this indicator is WORSE than the state value, but the difference IS NOT statistically significant.
- Reason for Concern = The county's value on this indicator is WORSE than the state value, and the difference IS statistically significant.
The county value is considered statistically significantly different from the state value if the state value is outside the range of the county's 95% confidence interval. If the county's data or 95% confidence interval information is not available, a blank gauge image will be displayed with the message, "missing information."NOTE: The labels used on the gauge graphic are meant to describe the county's status in plain language. The placement of the gauge needle is based solely on the statistical difference between the county and state values. When selecting priority health issues to work on, a county should take into account additional factors such as how much improvement could be made, the U.S. value, the statistical stability of the county number, the severity of the health condition, and whether the difference is clinically significant.
Why Is This Important?
In New Jersey, 7,855 women were diagnosed with breast cancer in 2018. Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women in the United States, other than skin cancer. It is the second leading cause of cancer death in American women, after lung cancer.Risk and Resiliency Factors
According to the [https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/hp/breast-prevention-pdq National Cancer Institute], the major risk factors for breast cancer are '''female sex''' and '''increasing age'''. Women with '''dense breasts''' have an increased risk proportionate to the degree of density. Among women with a '''family history of breast cancer''', risk is doubled if a single first-degree relative is affected and risk is increased fivefold if two first-degree relatives are diagnosed. Also, the lifetime risk is 55% to 65% for '''BRCA1''' mutation carriers and 45% to 47% for '''BRCA2''' mutation carriers compared to a lifetime risk of 12% in the general population. Reproductive risk factors: Women who have a '''full-term pregnancy''' before age 20 years have a 50% decrease in breast cancer risk compared with nulliparous women or women who give birth after age 35 years, and women who practice '''breast-feeding''' have a 4% decrease in risk of breast cancer for every 12 months of breast-feeding in addition to 7% for each birth. Also, undergoing oophorectomy or other forms of '''premature menopause''' may reduce breast cancer risk as much as 75% depending on age, weight, and parity, with the greatest reduction for young, thin, nulliparous women. Conversely, women who experience '''menarche at age 11 years or younger''' have about a 20% greater chance of developing breast cancer than do those who experience menarche at age 14 years or older. Behavioral risk factors: [https://www-doh.state.nj.us/doh-shad/query/builder/njbrfs/AlcoholChrnHvy/AlcoholChrnHvyCrude11_.html Alcohol consumption] is associated with increased breast cancer risk in a dose-dependent fashion and '''obesity''' is associated with an increased breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women who have not used combination hormone therapy (although it is uncertain whether either reduced alcohol consumption among women who are heavy drinkers or weight reduction among obese women decreases the risk of breast cancer). Conversely, '''exercising strenuously''' for more than 4 hours per week is associated with an average RR reduction of 30% to 40%. (The effect may be greatest for premenopausal women of normal or low body weight.) [Last reviewed: 1/26/20]How Are We Doing?
Between 1990 and 2018, the average age-adjusted breast cancer rate in females was 135.7 per 100,000. During the same time period, the age-adjusted breast cancer rate for women age 50 and older decreased from 397.5 cases to 361.1 cases per 100,000. The lifetime risk of developing breast cancer is 1 in 8 for women and 1 in 769 for men.What Is Being Done?
A Comprehensive Cancer Control Plan was developed by the Task Force on Cancer Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment in New Jersey which aims to reduce the incidence, illness and death due to cancer among New Jersey residents. [https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/ncccp/ccc_plans.htm]Related Indicators
Risk Factors:
- Physical Activity-Adult Prevalence
- Physical Activity Among Adolescents in Grades 9 to 12
- Cigarette Use among High School Students
- Obesity Among Adults
- Cigarette Smoking Among Adults
- Radon Mitigation
- Breastfeeding Initiation and Continuation
Health Status Outcomes:
Note
Incidence rates (cases per 100,000 population per year) are age-adjusted to the 2000 US standard population (19 age groups: <1, 1-4, 5-9, ..., 80-84, 85+). Rates are for invasive cancer only (except for bladder cancer which is invasive and in situ) or unless otherwise specified. Number of cases (numerator) is the total count of cases in five years.Data Sources
NJ State Cancer Registry, Nov 16, 2020 Analytic File, using NCI SEER*Stat ver. 8.3.9, [https://seer.cancer.gov/seerstat/] NJ population estimates as calculated by the NCI's SEER Program, released February 2021, [https://www.seer.cancer.gov/popdata/download.html]Measure Description for Incidence of Breast Cancer in Females
Definition: Incidence rate of invasive breast cancer in females for a defined population in a specified time interval. Rates are age-adjusted to the 2000 U.S. Standard Population. Rates are per 100,000 population.
Numerator: Number of new cases of breast cancer in females among a defined population in a specified time interval.
Denominator: Defined population in a specified time interval.

